DNA – The Molecule of Life
7 Topics | 6 Quizzes
Chromosomes, Diploid Cells and Haploid Cells
7 Topics | 6 Quizzes
Cell Division – DNA Replication, Mitosis and Meiosis
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Genes, Genotype and Phenotype
7 Topics | 6 Quizzes
Dominance, Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
4 Topics | 3 Quizzes
Sex-Linked Inheritance
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Punnett Squares
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
Mendelian Genetics
6 Topics | 5 Quizzes
Pedigree Charts
10 Topics | 9 Quizzes
Genetic Mutation
6 Topics | 5 Quizzes
Genetic Variation and Change
8 Topics | 7 Quizzes
Evolution – The Process
9 Topics | 8 Quizzes
Evolution – The Evidence
6 Topics | 5 Quizzes
7 | Summary

7 | Summary
Summary
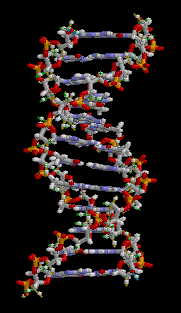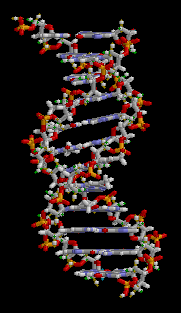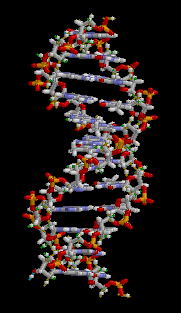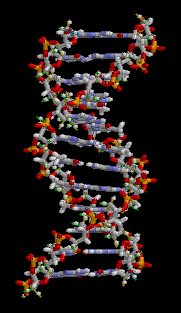
- Living things carry genetic information in large molecules called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid ), which is packaged into chromosomes in the nuclei of cells.
- DNA molecules are made up of subunits called nucleotides, which consist of a sugar, a base and a phosphate.
- There are four different nucleotides in DNA, each with a different base – G, C, A or T.
- Nucleotides can join together in two ways.
- Firstly, nucleotides can join by phosphodiester bonds (covalent bonds) between sugars and phosphates, resulting in single-stranded DNA.
- Secondly, nucleotides can join by hydrogen bonds (weaker bonds) between bases, resulting in double-stranded DNA.
- The hydrogen bonding between bases on different strands of DNA occurs according to the base-pairing rules – only G-C and A-T pairs can form.
- Double-stranded DNA molecules have a twisted structure known as a double helix.
- The order of the four different nucleotides in DNA molecules determines the genetic make-up of an organism.
(Image: brian0918, Wikimedia Commons)
